We often talk about the usefulness of data in making investment decisions. Basing investments on trusted data is an important step for any crypto investor. This applies to both on-chain and off-chain data and understanding both is a necessity for anyone planning on investing in or trading cryptocurrencies.
On-Chain Data
To keep it simple, “on-chain” data is everything recorded and stored immutably on the blockchain. This includes wallet addresses, transactions, transfers, and any other information that is stored in blocks. All this information is collected from blockchain nodes and is fully viewable through various blockchain explorers. On-chain data is the most widely used in crypto analysis.
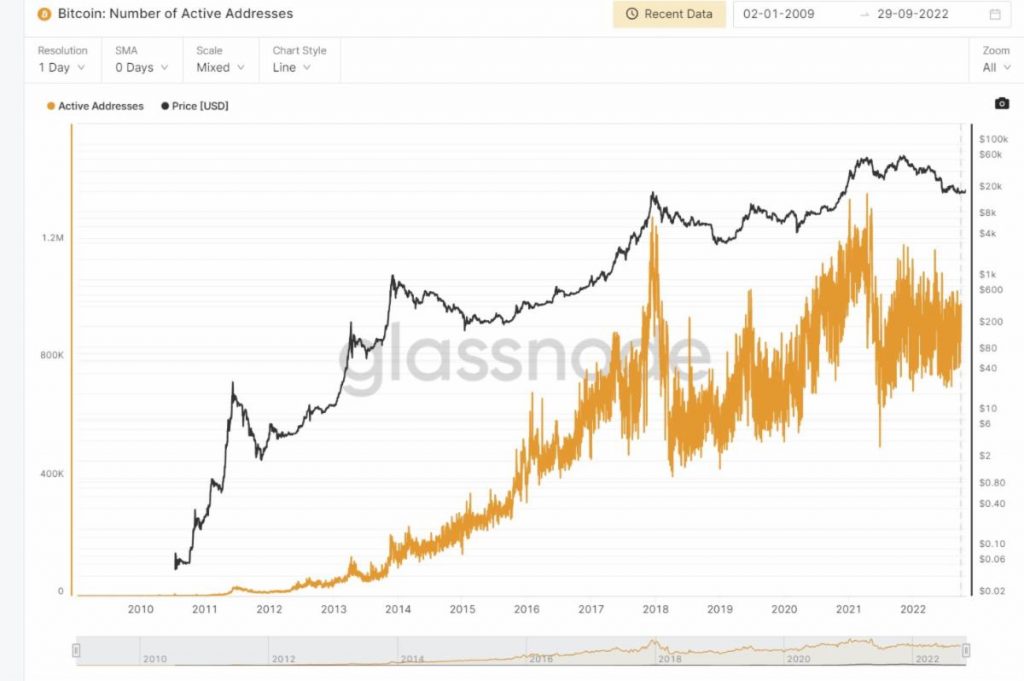
On-Chain Transaction Benefits:
- Security: Because blockchain data is encrypted and immutable, it is generally trustworthy and secure.
- Decentralization: The lack of centralization makes blockchain data trusted as there are no third parties that might manipulate the data.
- Transparency: Because blockchains use distributed ledger technology, every transaction is recorded and validated in multiple locations simultaneously. This allows for independent verification of transactions.
On-Chain Transaction Downsides:
- Slow: Blockchain transactions can be slow if network congestion increases due to spikes in the volume of transactions waiting to be processed.
- High Network Fees: Increased transaction volumes can lead to increased network fees. This can make transacting on the blockchain an expensive proposition at times.
- Energy Usage: Blockchains using proof of work for consensus are known to use a great deal of energy in the mining process.
Off-Chain Data
Off-chain data is data that’s created but not stored on the public blockchain.
The best-known example of off-chain data is the use of central order books by crypto exchanges. They need order book data to match sellers with buyers and to execute trades, but the data is not written to the blockchain. Instead, it’s held by a centralized crypto exchange, and it’s up to the exchange how much of this data will be publicly available. The great thing about this type of data is it’s specialized and allows for the creation of crypto indices, reference rates, and other market data products.
“Off-chain” could also mean the data is not on a public blockchain. There are many private blockchains that act like private cloud storage, thus allowing organizations to store blockchain data privately.

Off-chain transactions have great value for organizations. Not only do they often have the security afforded by the blockchain, but they have increased security because they’re private.
They’re also not subject to the transactional speed limitations often found with on-chain transactions. It’s known that most blockchains have problems with transaction speeds because of confirmation processes. Off-chain transactions sidestep issues associated with requiring confirmation from all blockchain participants. They are thus faster when compared with on-chain transactions. As these off-chain systems are usually not public-facing, they can be more secure.
Off-Chain System Benefits:
Faster Transaction Speeds: Because off-chain transactions don’t need to wait for confirmations from blockchains, they’re much faster. In some cases, they’re even instantaneous.
Lower Cost: Because off-chain transactions don’t require validation through mining or staking, there are few fees (or zero fees).
Greater Anonymity: Since off-chain transactions don’t get broadcast to the public blockchain, they offer greater privacy.
Off-Chain System Downsides:
Less Transparency: Off-chain transactions lack transparency. This could lead to disputes regarding their validity.
Third-Party Trust Issues: A lack of consensus methods means validation may be in the hands of third-party intermediaries. This can lead to trust issues.
Potentially Less Secure: Data outside the immutability of the blockchain is more vulnerable to manipulation. This could lead to fraud.
When analyzing any crypto project, both on-chain metrics and off-chain metrics can be useful. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of both can help to determine the weight given to each type of data during this analysis.
Crypto Analysis with On-Chain and Off-Chain Data
On-chain data is more commonly used in analysis, particularly when looking at market sentiment. As on-chain data looks specifically at real-time transactions and balances, it can be very useful in determining whether a token is a good investment or not at any given time. If a token is controlled by a small number of whale accounts or is thinly traded, it may be a poor investment choice.
Off-chain data can be equally useful in crypto analysis if the third-party storing and providing that data is trustworthy. Level 2 solutions like the BTC Lightning Network or Optimism for Ethereum add to the utility of their respective blockchains. As these solutions see increased usage, the data collected from them can help determine whether a certain token is a good investment choice.
Useful On-Chain Tools
For raw data, blockchain explorers like Etherscan for Ethereum or Solscan for Solana are the gold standard. They let you view all the data stored to a blockchain including transactions, wallet addresses, smart contracts, and NFTs. However, they only provide raw data. More useful to average investors are the tools that aggregate the data to make sense of this information.
A number of useful analytics platforms have sprung up that can help make sense of the vast amounts of data stored on blockchains. Some are free have become go-to sources for coherent data regarding blockchain activity. Some of the more popular analysis platforms include:
- Glassnode
- IntoTheBlock
- Nansen
- Dune Analytics
- Messari
You’ve likely seen data and charts from several of these platforms included in previous BMJ newsletters and blog posts, and for good reason. They’re the top data providers and have become trustworthy in terms of the data they provide.
We’ll look deeper into ways all this on-chain data can be used in one of our future BMJ columns. In the meantime, it could be worth your while to go explore the analytics platforms above.
Investor Takeaway
You can find great utility in both on-chain and off-chain data depending on your use case. Understanding the strengths and weakness of each is a good starting point for those looking to do their own research and analysis of various blockchain projects and cryptocurrencies.
While on-chain data is considered the gold standard for crypto analysis, there’s much to be said for off-chain data as well. Without off-chain data, we couldn’t have indices, reference rates, or other crypto market products.
Just as a combination of fundamental and technical analysis can help when researching an asset, a combination of on-chain and off-chain data can be helpful for analyzing crypto and blockchain tokens.